Old Fashioned Black and White Color Wheel Test Pattern

The RCA Indian-caput test pattern
The Indian-head test pattern is a test carte that was introduced in 1939 by RCA of Harrison, New Bailiwick of jersey, for calibration of the RCA TK-1 monoscope. It was widely used by idiot box stations worldwide during the black-and-white television dissemination era. It features a drawing of a Native American wearing a headdress along with numerous graphic elements that test different display aspects.
As television broadcasting ritual [edit]
The Indian-head examination pattern became familiar to the large baby boom TV audiences in America from 1947 onwards; information technology would frequently follow the formal television receiver station sign-off after the United States national anthem. The Indian head was also used by the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation (CBC)[1] in Canada in conjunction with its own monochrome test design, following the Canadian national anthem sign-off in the evening, and during its final years in the tardily 1970s and early 1980s it was shown before sign-on in the morning time, subsequently the showing of the SMPTE color bars.[2] It was as well used by Rhodesia Television (RTV) during British colonial times (varying between Northern and Southern Rhodesia) following the playing of "God Salve the Queen" at closedown. This test blueprint was later used by the Venezuelan Tv aqueduct Venevision, in conjunction with the RMA Resolution Chart 1941, in the mid and belatedly 1970s before signing on with the Venezuelan national anthem. Telesistema Mexicano (now Televisa) stations besides used this examination pattern until the late 1960s immediately later playing the Mexican national anthem at sign-off. In Sweden the Indian caput was used in examination transmissions from the Purple Institute of Applied science alongside the RMA Resolution Chart 1941, Telefunken T05 test card, likewise equally other experimental examination cards from Televerket and Chalmers University of Technology from 1948 until Nov 1958 when it was replaced past the Sveriges Radio TV (at present Sveriges Television) test carte du jour.[three] [four] Saudi Dissemination Authorisation in Kingdom of saudi arabia likewise formerly used a modified version of the Indian caput examination pattern, with the Emblem of Saudi arabia replacing the Indian head drawing,[5] from 1954 until 1982 when it was replaced with a heavily modified Philips PM5544 examination card. The Indian head was also used in Brazil by Rede Tupi, both equally a test pattern and as part of a idiot box ident, from its launch in 1950 until it became the starting time Brazilian television network to adopt colour goggle box in 1971–1972.
The Indian-head design could variously exist seen afterwards sign-off only while the station was even so transmitting; while transmitting prior to a typical via.m. formal sign-on; or even during the daylight forenoon hours on newer low-upkeep stations, which typically began their broadcast day with midday local programming around 10 or xia.m.[vi]
During the late 1950s the test pattern gradually began to be seen less ofttimes, after fewer sign-offs, on fewer stations, and for shorter periods in the morning, since new and improved TV broadcast equipment required less adjusting. In later years the test pattern was transmitted for equally little as a infinitesimal later studio sign-off while the transmitter engineer logged required Federal Communications Commission-US/Industry Canada transmitter readings before cut power.[ commendation needed ]
Past the end of the Indian-head TV era in the tardily-1970s/early on-1980s, there was no nightly test pattern on stations where automatic logging and remote transmitter controls allowed shutdown of power immediately after the formal sign-off. After an firsthand transmitter ability off, in lieu of the Indian-head test pattern and its sine wave tone, a Television set viewer heard a loud audio hiss like FM radio interstation noise and saw the video noise. Audio and video dissonance received on Indian-head era Idiot box sets respectively indicated the absence of analog audible and visual broadcast carriers. Home-use TVs typically did not take a no-signal noise muting and blanking feature until the late analog TV flow.
When US broadcasters switched to color tv set, the SMPTE color confined largely superseded the black-and-white test pattern image although a few station owners employed colorized versions of the NBC/CBS "bullseye" test pattern, in some cases lasting until as recently equally the early 1990s.[ citation needed ]
Generation [edit]
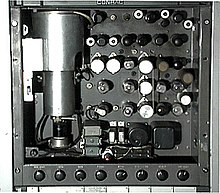
The RCA TK-1C monoscope camera that generated the examination blueprint
The Indian-caput test pattern was not generated past pointing a photographic camera at a card, as many older exam patterns were. Rather, it was generated directly as a monochrome video betoken by means of a monoscope tube, a specialized video camera tube with the design built into the tube.
An RCA TK-1 test design generator (monoscope) is a nineteen-inch rack-mounted chassis, which contains a monoscope tube[vi] housed inside an anti-magnetic steel shield[seven] and associated electronic circuits for driving it. The monoscope tube is constructed similarly to a pocket-sized cathode ray tube (CRT), only instead of displaying an image, information technology scans a congenital-in paradigm, producing a video bespeak. The tube has a perfectly proportioned copy of the test blueprint principal art inside, permanently deposited equally a carbon paradigm on an aluminum target plate or slide.[a] This perfect copy allowed all of the boob tube studio and production control room video monitors, and home television receiver sets, to exist identically adjusted for minimal distortions such every bit ovals instead of circles.[b] When the monitor or TV set was correctly adapted to show test pattern circles, the received picture's attribute ratio was exactly four units wide past 3 units high.
Use [edit]

Indian Caput blueprint with its elements labeled, describing the use of each element in aligning a blackness and white analog TV receiver.
The graphic of the Indian and all of the patterns on the chart served specific purposes. With the chart, many typical daily (sometimes hourly) adjustments on cameras, home, and studio monitors could exist made. An experienced circulate engineer could glance at the drawing of the Indian Chief and apace know if everything was working correctly or if more careful aligning was needed. Within the chart, the tools necessary to adapt perspective, framing, linearity, frequency response, differential proceeds, contrast and white level (brightness) are all provided. The grid and circles were used for perspective, framing and linearity. The tapered lines (marked with twenty, 25, 30, and 35) were used for resolution and frequency response. The sparse lines marked from 575 to 325 on ane side and 300 to l on the other side referred to lines of resolution. The greyness bands emerging from the center off to the lower correct and upper left were for differential gain, contrast, and white level.
Merely subsequently the monitors were adjusted was an actual Indian-caput test design used. A cardboard mounted lithograph of the test pattern was typically attached to a rolling vertical easel in each Tv set studio, to be videographed by each studio photographic camera during examination time. And so the cameras were adjusted to appear identical on picture monitors, by alternately switching between and comparing the monoscope image and the examination card prototype. Such adjustments were fabricated on a regular basis because television arrangement electronics then used hot vacuum tubes, the operating characteristics of which drifted throughout each broadcast twenty-four hours.[ citation needed ]
Exam patterns were as well broadcast to the public daily to allow regular adjustments by domicile television owners and Telly shop repair technicians.[6] In this regard, various features in the design were included to facilitate focus and contrast settings, and the measurement of resolution. The circular "bullseyes" in the centre and the four corners permitted uniform deflection yoke and oscillator amplitude adjustments for centering, pincushioning, and image size.
The test pattern was usually accompanied by a 1,000 or 400 hertz sine wave test tone, which demonstrated that the Tv aural receiver was working. If the tone was pure-sounding rather than a buzz or rattle, then transmitted speech and music would non be distorted. 400 Hz is somewhat less annoying for technicians to hear for extended work periods.[eight]
As a cultural icon [edit]
An actual Indian-head exam card, the design as printed on art-grade white cardboard, was but of secondary importance to television organization adjustment, but many of them were saved every bit souvenirs, works of found object art, and inadvertent mandalas. By contrast, nearly all of the difficult-to-open, steel-shielded, vacuum glass monoscope tubes were junked with their hidden Indian-caput test pattern target plates still inside. The monoscope target plates were as well pocket-sized, a few inches in size, while the camera test cards were 1.five past 2 feet (0.46 by 0.61 m), appropriate for moving picture-framed wall display.[ commendation needed ]
The original fine art work for the Indian chief portrait was completed for RCA's research engineers past an artist named Brooks on August 23, 1938. The original portrait was done in pencil, charcoal, ink and zinc oxide. For almost a year the Indian portrait was televised in the laboratory every bit the unabridged exam design. It was later incorporated into the pattern of calibrated lines and shapes. The original portrait measures eight inches (twenty cm) across as a round image containing several identifiable shades of gray, and some detail in the feathers. There is besides some Zone 8 texture in the white feathering and some Zone ii texture in the black hair. The primary art for both the portrait and the design design was discovered in a dumpster past a wrecking crew worker as the erstwhile RCA manufacturing plant in Harrison, New Jersey was being demolished in 1970. The worker kept the art for over 30 years earlier selling it to goggle box engineer and collector Chuck Pharis.[nine]
The Indian-head test pattern became obsolete in the 1960s with the debut of color television; from that point onward, an alternating exam card of color bars became the test carte du jour of choice. Since the 1990s, most television stations in the U.s.a. have broadcast continuously without regular sign-offs, instead running infomercials, networked overnight news shows, syndicated reruns, cartoons, or erstwhile movies; thus, the broadcast of examination patterns has become mostly obsolete (though they are nonetheless used in postal service-production and broadcast facilities to check color and signal paths). Nevertheless, the Indian-head examination pattern persists as a symbol of early tv set. A variant of the card appeared on theatrical release posters for "Weird Al" Yankovic'southward 1989 moving picture UHF. Information technology was sold as a night-light from 1997 to 2005 by the Archie McPhee company,[10] reminiscent of the times when a fairly common late-night experience was to fall asleep while watching the tardily motion-picture show, only to awaken to the feature sine wave tone accompanying the Indian-head test pattern on a black-and-white Idiot box screen. The exam menu also featured in the opening sequence of the early 1960s science fiction anthology The Outer Limits.[11] Decades later on, information technology was popularized equally the loading screen for the Fallout series video games, and a part of the Electronic Frontier Foundation's website.[12]
Many U.S. television stations chose the paradigm of the Indian-head bill of fare to be their last epitome broadcast when their analog signals signed off for the final time between February 17 and June 12, 2009, as function of the The states digital television transition.[ citation needed ]
Notes [edit]
- ^ The target plate is sequentially scanned with a focused beam of electrons, which were originally called cathode rays. When the electron beam strikes the carbon image areas, the carbon resists current flow, and the resulting lower electron electric current period is adjusted to announced equally video black. When the electron axle strikes the metallic-aluminum image areas, at that place is less resistance with higher current flow, and the resulting college electron current flow is adjusted to announced as video white.
- ^ Analog television on cathode ray tubes besides needed to be adjusted for vertical and horizontal linearity. An error in vertical linearity (such as the top of the picture stretched with the bottom squashed) might get unnoticed on the SMPTE color bar design, just would instantly plow a circle into an egg-shape.
References [edit]
- ^ "CBC-Goggle box Test Pattern Explained p12-13". 22 April 2012.
- ^ MTLTV (28 September 2012). "Tête de l'indien". Archived from the original on 2021-12-22 – via YouTube.
- ^ erikbe99 (9 July 2007). "Testbilder genom tiderna". Archived from the original on 2021-12-22 – via YouTube.
- ^ "Svenska: Radiochefen i Göteborg Nils Dahlbeck". 1957.
- ^ Archived at Ghostarchive and the Wayback Motorcar: "saudi tv exam pattern (1965)". YouTube.
- ^ a b c Kay, M. S. (January 1949). "The Television Test Pattern" (browse). Radio & Television News. Ziff-Davis. 41 (i): 38–39, 135–136 – via Wikimedia. "Every television station, prior to its actual broadcasting flow, transmits a examination design for the purpose of permitting set owners to arrange their receiver controls for optimum reception." The article besides states that television programming (in 1949) was only a few hours each evening. The Indian-head test blueprint was built into the RCA "monoscope" tube, a 2F21, which acted every bit a complete replacement for the TV photographic camera.
- ^ "Chuck Pharis Spider web Folio: Featured article". world wide web.pharis-video.com.
- ^ 1,000 Hz is the standard 0dB (0 decibel) reference point for analog-NTSC Television set audible system frequency response measurements, just for elementary line-reference 0dB sound level setting, preference for hearing 400 Hz is common knowledge and feel among broadcast and audio technicians. "From the factory the frequency of the reference tone is configured to be 400 Hz. This is a prissy alternative to the more than typical ane kHz, a frequency which can before long become very annoying to a listener's ears. In most cases 400 Hz volition be perfectly acceptable, and actually preferred." - Model 742 Audio Mixer User Guide, Upshot 2, May 2005 (PDF) Archived 2006-12-17 at the Wayback Machine; p.10 - Studio Technologies, Inc.
- ^ "Chuck Pharis Web Page : The Indian Head Test Pattern Story! , Updated April 29, 2017". www.pharis-video.com.
- ^ The Indian-head examination pattern night low-cal was included in a set of three novelty night lights with test pattern lamp shades: RCA TK-1 Indian head (1950s), SMPTE color confined (1960s), and an Emergency Broadcast System (EBS) Idiot box-examination slide image ("This is a test! This is just a test!") from the centre Cold War era.According to the customer service section of Archie McPhee company, Seattle, Washington, the set of iii, as Item #10480, was sold from 1999-01-11 to 2005-06-17. Their representative said these lamp shades were created by the company, and not obtained from an outside source. (Source accessed by phone on 2007-eleven-07).[ original research? ]
- ^ chicagosundials (19 November 2008). "The Outer Limits Intro". Archived from the original on 2021-12-22 – via YouTube.
- ^ "The Most Litigious Dessert in America". eff.org. 5 May 2013.
External links [edit]
- "The Indian Caput Exam Pattern original primary art". Archived from the original on June xv, 2015. Retrieved May 18, 2006.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) – rescued from an RCA dumpster in 1970 - Picture and detailed clarification of an RCA TK-1 examination design generator (monoscope)
- mire.project – Street art work most exam patterns
0 Response to "Old Fashioned Black and White Color Wheel Test Pattern"
Post a Comment